IP Search / Analytics
PINTAS conducts multi-tier search strategies on a variety of paid and free IP databases to perform extensive and comprehensive searches to uncover the most relevant IP prior arts to meet your requirements.
PINTAS IP Search/Analytics takes stock of your and your competitors’ intellectual property assets and capabilities


Contact Us
IP Finance
Under PINTAS IP Finance, we raise funds through securitization of your intellectual property assets.
Owners of IP assets can raise money to fund the development and commercialisation of their IP assets through a multitude of channels. The funding ecosystem summarises the funding options available to IP owners in different stages of development of their IP assets, from birth of an idea to development and eventual commercialisation of the ideas
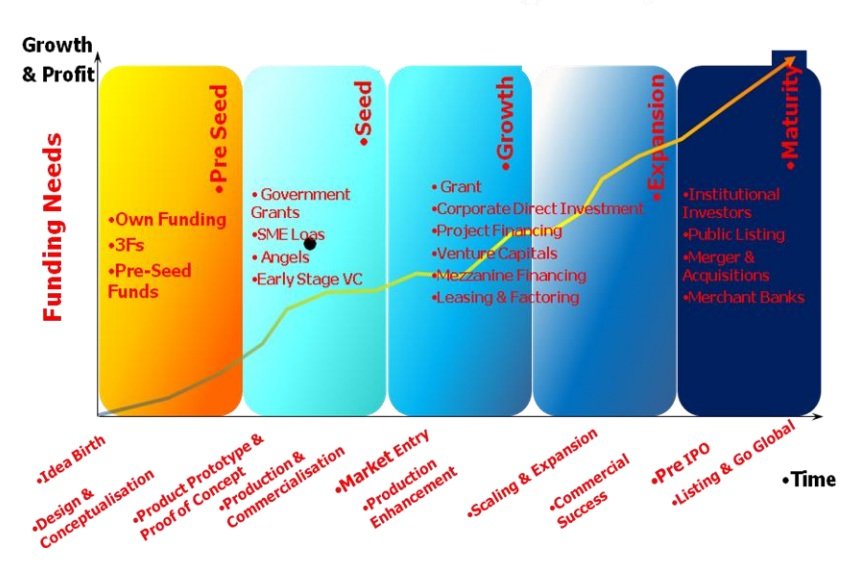
Diagram 2.5.1 summarise the IP Funding ecosystem
There are basically three sources of funding for IP Owners, namely government grant, equity financing and debts financing.
(A) Grant Financing
The contributions of IP based entrepreneurship (or technopreneurship) in spurring economic growth, creating high income jobs and new industries which generating high returns are widely acknowledged.
To encourage the development of technopreneurship, many governments have come out with grant and financial incentive scheme for development and commercialisation of IP assets. The grant scheme aim to provide generous low cost fundings to qualified technopreneur to kick start their ventures.
The sources of grant in Malaysia are:-
- Matrade
- Malaysian Biotechnology Centre
- Malaysia Technology Development Centre
- Mimos Berhad
- Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation
- Ministry of Entrepreneur and Co-operative Development
- Small and Medium Industries Development Corporation
- Multimedia Development Corporation (MDeC)
- Cradle
These fund providers are mandated by the government to offer different types of grants to IP owners in different phases of IP development, namely from creation, commercialisation to market enlargement of their IP assets
Amongst the keys things to look at in applying for IP Grant are:-
- Focus of the grant
- Eligibility
- Percentage of funding
- The unwritten rules (what can be claimed, the fine print, when to incur etc)
- How to maximise your amount
- How to shorten your time
(B) Debt Financing
Consider the means, targets, timing, cost, etc
P Owners can also avail themselves to debt financing as a source of funding to finance the development of their IP based business ventures. In certain jurisdiction like US and China, IP assets can be used as collateral to secure loan from banks. However, as banks are generally more risk adverse, debt financing are more common at the later stage of IP development, usually at the growth stage of a IP based business venture as illustrated by Diagram 2.5.2 below.

Diagram 2.5.2, Source: TEN3COACH
(C) Equity Financing
Another important source of financing of IP based business ventures is equity investment from angels, venture capital or private equity players. Angles are affluent individuals who invest in seed or early start ups, venture capital provides equity funding to early stage technopreneur ventures while private equity back established enterprise using a combination of debt and equity.Venture capital bridges IP owners and technopreneurs with the much need start up capitals and business know how in a combination whuch is capable of great value and wealth creation. Spectacularly successful companies like Amazon and Google are made possible by venture capital investment. Diagram 2.5.3 summarises how huge wealth was created by Venture Capital investment in the case of Amazon.com

Diagram 2.5.3, Source: TEN3COACH
IP Friendly Stock Exchanges
IP Based Enterprises can also raise funding from the general public by listing their IP holding companies in some of IP friendly stock exchanges in the region. The quantitative and qualitative criteria for IPO in Malaysia, Singapore and Hong Kong are summarised as follows:-
1. Quantitative Criteria
2. Qualitative Criteria
- STRENGTH AND INTEGRITY OF PROMOTERS & MANAGEMENT
Strong background & experience. - BUSINESS MODEL
Unique features / competitive edge over competitors. - BUSINESS PROSPECTS
- R&D CAPABILITIES
- INTELLECTUAL CAPITAL
- STRATEGY & EXECUTION
- CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
There are many advantages as well as considerations for IP Based Ventures to raise funds through public listings. The Pros and Cons of public listings can be summarised as follows:-
Advantages
- Access to capital – for growth & expansion, retiring existing debts, corporate marketing and development, acquisition capital and corporate diversity
- Correct Valuation – share price
- Compensation – to attract & retain talented employees via performance based incentive
- Brand Value – prestige, image and publicity
- Merger & Acquisitions – expansion
- Exit Strategy – offering reward & financial freedom for the founders & employeesse
Considerations
- Disclosure of information – public disclosure eg shareholding pattern, quarterly & annual financial statement, profile of directors, etc
- Decision take time – BOD approval
- Cost of IPO – one time expenditure
- Complication of operation
Contact Us
IP Structure
The objectives of IP Audit are:-
PINTAS IP Structure Service seeks to devise and implement an optimum corporate structure for IP based companies through the setting up of Intellectual Property holding companies incorporated in selected offshore jurisdictions in order to make the companies eligible for a minimum rate of withholding tax, little or no tax in the country of residence of the licensor or the property, and little or no withholding tax in the countries through which the intellectual property is licensed.
Background:-
In the absence of careful planning, owners of intellectual property can find their profits seriously eroded by both taxes on profits and by withholding taxes.
IP as the Engine of Growth in Knowledge Based Economy:-
In the knowledge based economy of today, there is a growing trends to focus more on IP related activities, like brand building and R&D. Limited value added manufacturing activities, are routinely outsourced to third world countries. The value shifting trends can be illustrated by the diagram below.

For example, IP based companies like Nike has been actively outsourcing its manufacturing activities to low cost countries like Vietnam, China and Indonesia while at the same time spending millions developing, owning and promoting its brands and innovative designs.The establishment of IP holding company, therefore, is to capture the centre of gravity of corporate value is entirely consistent with the general value shifting trends in our knowledge based economy.
Tax Planning Through IP Holding Company:-
To achieve greater tax efficiency for the group, an IP Corporate Structure, which involves the establishment of a special purpose vehicle that holds all the vital IP assets of the company as shown in Diagram 2.1 is proposed.
The IP holding company will preferably be set up in jurisdictions that levy minimum taxation (usually less than 10%) for all royalty income accruing to the IP assets owned by the IP holding company. For greater tax saving, an intermediary company established in a tax treaty jurisdiction can be utilized to minimize withholding tax exposures suffered by payers of royalties. In the structure proposed, the IP holding company will emerge as a profit centre for the group where profits generated by the group operation will be parked. The other activities of the group like marketing and sale, manufacturing and production as well as research and development will be reduced to cost centers. One good example is the tax planning model by IKEA ( see Table 2.2)
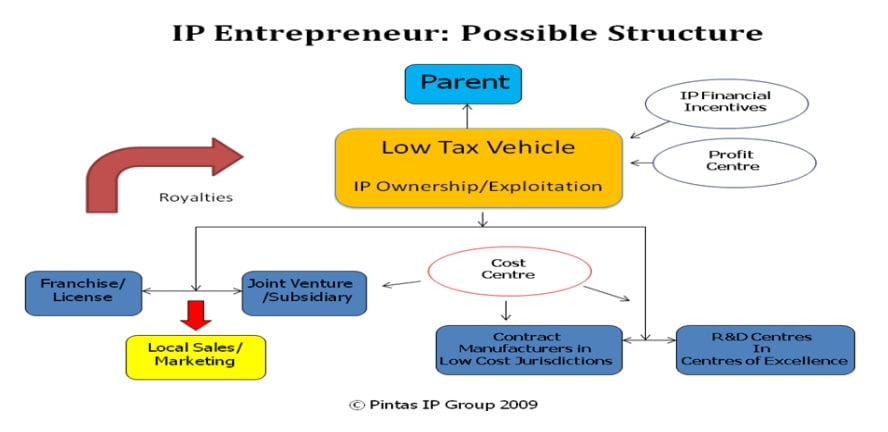
Table 2.1: IP Holding Company

Table 2.2 IKEA Tax Model
Advanced Royalties Planning Through Intermediate Royalty Holding Company:-
Traditional royalty tax planning has involved transferring intellectual property (IP) to a company in a jurisdiction that imposes low tax or no tax on profits. However countries from where royalties are paid generally levy a withholding tax that can be as high as 30%.
It is important to take into account that if IP is transferred after it has become valuable, it likely that there will be capital gains tax implications on the disposal of the IP to the low tax company. It is therefore preferable to aim to transfer the IP to the intellectual property holding company while it is at a low value, or, alternatively, to ensure that the IP is developed by the company that is to ultimately own it.

Diagram 2.3 Royalty Planning: A Basic Structure
In the example shown in Diagram 2.3 above, ownership of the IP is held in an offshore jurisdiction where the tax rate on profits is zero. The offshore jurisdiction grants a sub licence to an intermediate royalty holding company in a tax treaty jurisdiction, which, in turn, licences the IP to a third party.
The Importance of Double Taxation Treaties:-
If a double taxation treaty exists between two jurisdictions, when royalties are paid the withholding tax rate will be no greater than the rate specified in the tax treaty between the tax treaty jurisdiction and the country paying the royalty. This rate is generally significantly lower than the standard withholding tax rate.
Intermediate Royalty Holding Company Location:-
The jurisdiction for the location of an intermediate royalty holding company should offer the following beneficial features:-
- Access to a large network of double taxation treaties
- Low corporate tax rate liability on royalties received
- The ability to pay-on royalties without withholding tax
- The eligibility of royalty payments as a deductible expense against royalty receipts
- The ability to get tax rulings on the margin to be retained in the intermediate company
Contact Us
IP Enforcement
PINTAS IP Enforcement helps IP Owners to proactively protect their profit margin and market share from copycats through effective enforcement tactics. We help to ensure that the interests of IP Owners are protected in the market.
PINTAS IP Enforcement helps IP Owners to proactively protect your profit margin and market share from copycats through effective enforcement tactics

We assist IP Owners in enforcing their rights and take actions against any misuse of their IP, counterfeits and infringements. The scope of IP Enforcement includes
SCOPE OF SERVICES


Contact Us
IP Training & Event
We help IP rich ventures to monetize and leverage on their IP assets through IP education and training. We design, manage and deliver customized training events and training program to promote and commercialize your IP assets.
IP Training & Education
Through in-depth IP seminars and customized workshops, we share the latest best practices and trends on IP monetization and IP protection. The IP training and education is carried out by IPACADEMY, the dedicated IP training arm of PINTAS.
We Design, Manage And Deliver Customised Training Events and Training Program To Promote And Commercialise Your Intellectual Property Assets.

IPSPACE ACCELERATOR
Pintas assists deep tech IP ventures to accelerate and scale up their operations in the China Asean region through IPSPACE China Asean Technology (CAT) Accelerator Program, a project jointly curated with IPTECH.

An acceleration program for IP rich technology venture from Southeast Asia and China regions to establish market-product fit and scale up in China-Asean markets.
Contact Us
IP Tax
Tax / Royalty Planning at 3 different situations
- New IP assets creation (development Stage)
- Acquisition of IP assets
- Existing IP assets owner in respect of revenue derived from IP Assets
A. Tax Incentives For Creation of IP Assets

A.1 Tax Holidays for Companies that create and commercialise new IPs
| MSC Status | – ICT and Multimedia related IPs – Tax exemption for 5 years extended to 10 years, or – 100% ITA on qualifying Capital Allowances for 5 years |
| Bionexus Status | – Biotechnology Related IPs – An exemption from tax on 100% statutory income for 10 years (new) or 5 years (existing) |
| Pioneer Status | – Promoted activities or products – Tax exemption of 70% of Statutory income for 5 years – 100% for company located in promoted location |
| Investment Tax Allowance | – Promoted activites or products – Tax exemption of 70% of Statutory income for each YA computed at 60% on Qualifying Capital expenditure within 5 years from the date which the approval take effect. – 100% for company located in promoted location |
A.2 Double tax deduction For IP Related Activities
1. Registration of patent, trademark and product licensing in Overseas
Cost of registration of patent, trademark and product licensing overseas
- For Malaysian resident company only
- Primarily and principally for the purpose of promoting the export of goods.
[Income Tax (Deduction for promotion of exports) Rules 2007.PU(A) 14/2007 Wef. YA2006]
2. Advertisement on Malaysia brand name goods
Advertising on Malaysian Brand name goods locally
- 70 % owned by Malaysian– Brand name owned by the company or its related company
- Product must be export quality standardAdvertising on Malaysian Brand name overseas
- Expenses on advertising of Malaysia brand names registered overseas; and
- Professional fees paid to companies promoting malaysia brand names
[Income Tax (Deduction for promotion of exports) Rules 2007.PU(A) 62/2002 Wef. YA2002]]
3. Research expenditure
Research Expenditure ( s.32A)
- Approved by minister. Or
- Undertaken by person participating in industrial adjustment.
- Incurred within 10 years from the date of approval
- Approved research project undertaken by a company either in-house or contracted to external research companies or institute.
- Expenses for use of facilities or services provided by the approved research institute
- Contribution in cash to approved research institute
B. Tax Planning for Acquisition of IP Assets
Purchase an IP and put to use will have a benefit over a period of time (ie.general revenue) and are therefore considered of a capital nature for tax purposes
- In general , cost of IP assets purchase is not subject to deduction or capital allowances!! (capital expenditure with no capital allowances)
- In budget 2008, there are tax deduction, 20% of the cost of purchase:
a) for locally incorporated company to acquire high tech assets
For production in Malaysia
To gain export market
b) For manufacturing Company to acquire IP “rights�?
for the use in manufacturing process.
a) For Locally owned Companies which acquire a foreign company to acquire high technology for production in Malaysia or to gain new export markets for local products
- Deduction for an amount = 1/5 ( 20% ) of the acquisition cost incurred for five years. , However, such acquisition must verified by MIDA
- Acquisition must be in the form of cash transaction and completed within 3 years– Not allow for the second acquisition by same Company.
- Acquisition cost include value of the share, Professional fees, stamp duty, traveling and accommodation
[Income tax(Deduction for Cost of Acquisition of a foreign Owned Company) Rule 2003, Amended Rule 2008]
b) The cost of acquisition of propriety rights** (IP) incurred by a manufacturing company for the use in manufacturing process
- 20% of the cost as deduction in the YA of purchase and 4 following YA against business income includes
- Acquisition cost of the propriety rights, consultancy and legal fees, stamp duty.
- 70% owned by Malaysian.
** Patent, industrial designs or trademarks[Income tax(Deduction for Cost of Acquisition of a foreign Owned Company) Rule 2003, Amended Rule 2008]
Tax Planning for Existing IP Owners
- Sell IP assets, or
- Generate income from IP assets (ie. Royalty Fee)
1. Outright Sale of IP assets
Outright sale of IP assets
- Capital Gain
- Not subject to Income Tax
- Under tax & Royalty planning scheme, to consider set up IPHC to in country of lower tax jurisdiction to acquire the IP assets
Outright sale of IP assets- Points to note:
- Willing seller willing buyer ( supported by agreement)
- Lump sum payment. If periodic payments, may subject to income tax
- Valuation of IP assets – future income/ cash flow projection
- Timing of disposal to maximum the value.
- set up IPC since day one, this allows sale of Company instead of sale of IP assets within Malaysia!
- Set up MSC status company, Bionexus Company
2. Royalties Planning
Generating Guidelines for Tax on “royalty fee�? from IP assets:
- Income (Royalty fee) received in Malaysia from resident is subject to normal income tax
- Scope of tax under S.4(d), Royalty is defined in S.2 of ITA
- Administration expenses to be deducted under normal business expenses. (To show that the company running the business)
- Remit income back into Malaysia – Foreign source of income received in Malaysia by a resident from outside Malaysia is exempted from tax ( para 28, sch 6) inclusive of dividend income and royalty income
The Scope of royalty is defined in Section 2 of the ITA as follow:-
a) any sums paid as consideration for the use, or the right to use
i) Copyrights, artistic or scientific works, patents, designs or models, plans, secret processes or formulae, trademarks;
ii) know-how or information concerning technical, industrial, commercial or scientific knowledge, experience or skill;
iii) income derived from the alienation of any property, know-how or information mentioned in para (a) of this definition
Royalty Planning – Points to note:
- Income from IP is not like income from a regular business. It is highly mobile and can be easily moved to another tax jurisdiction.
- MOVE the income to countries with lower tax by setting up IPHC at countries ( e.g Singapore/Hong Kong) with lower tax jurisdiction or tax free (eg) BVI and acquire the IP assets
Singapore Tax Rate
effective 2010, corporate income tax rate will be further reduced from 18% to 17%. In order to make Singapore as an attractive investment destination, income tax rates in Singapore have been going down consistently as seen below.
1997-2000 – 26% , 2001-2001 -25.5% , 2002-2002- 24.5%, 2003-2004 -22%2005-2006 -20% , 2007-2009 – 18% , 2010 17%
0% tax on S$100K taxable income for first three tax filing years for a newly incorporated company
8.5% tax on taxable income of upto S$300K
- Withholding tax 10% on royalty paid to non-residence – S109 /S15/S3/4(d) – final tax (as compared with 25% IT)
- Remit income back into Malaysia – Foreign source of income received in Malaysia by a resident from outside Malaysia is exempted from tax ( para 28, sch 6) inclusive of dividend income and royalty income
The Tax/Royalties planning structure for an existing IP Owner can be summarised by Diagram 2.6.1below.
Contact Us
IP Valuation
PINTAS IP Valuation traces your revenue back to your IP assets in order to account fairly and accurately the value of your IP assets
Generally, IP assets are difficult to value because of the following reasons:
- Historically, no public trading markets (eg property)
- Terms & Conditions vary widely.
- IP assets are inherently dissimilar
- IP transfers are often motivated by unique strategic considerations
- Details of IPR transfers are usually not widely disseminated
IP Valuation is not so much a matter of science but rather a matter of external judgement. The Foundation of IP valuation analysis consists of four constituent blocks, each with an associated question:
- Purpose – Why are we valuing the asset?
- Description – What is the asset?
- Application – How will the asset be used?
- Standard – Who is the assumed buyer of the asset?
There are many IP valuation methods in the markets as summarised in Diagram 2.7 below:-

In a nutshell, the most common valuation methods are based on one of the three methods below:-
A. Cost – Based on cost to replicate, (less functional or economic obsolescence) that is the cost to create or recreate the asset; we look at what we spent on developing the IP and what another company might spend if they were to invent it from scratch.
B. Market – Based on market transactions involving comparable assets (with adjustment for differences) that is the sales of comparable IP, where a “somewhat” similar deal could be used for the purposes of comparison.
C. Income – Discounted Net Cash Flow (royalties/profits/savings)
which is based on the future economic benefits produced by the intellectual property; where we look at the projected incremental profits or cost savings from using the IP.
For the purpose of discussion, we shall look at the Discounted Net Cash Flow Method. The Discounted Cash Flow Method involves a summation of the net cash flow derivable from an IP assets over its useful life and discount the value to the present day value using an effective discount rate. To do that, we need to
(a) Determine the overall cash flow of a company from P&L account
(b) Disaggregate the business segment and product line ( Diagram 2.7.1)
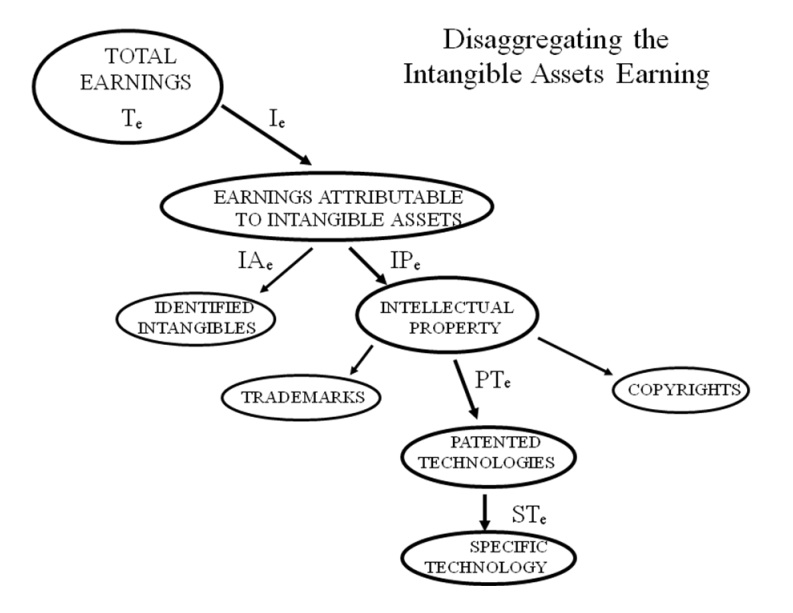
(c) Disaggregate the earnings of the relevent product line to derive the earning attributable to the intangible assets ( Diagram 2.7.2)
(d) Disaggregate the intangible assets earnings to arrive at the earning attributable to a particular IP asset. ( Diagram 2.7.3)
(e) The value of an IP Asset can be deduced using the formula:-

1. Identify incremental cash flows (x) for each period (n)
2. Select appropriate discount rate (r)
3. Calculate net present value
Diagram 2.7.4 gives an example of the application of the formula

Diagram 2.7.1


Contact Us
IP Capitalization
Through Pintas IP Capitlization, we help to make intellectual property the center piece of your corporate strategy
